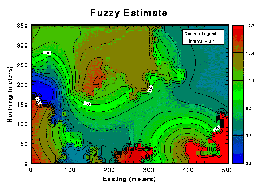
Synthetic Example (Part II)
Given this zonal distribution map from a conditional simulation, several different interpretations can be created by varying the boundary rules.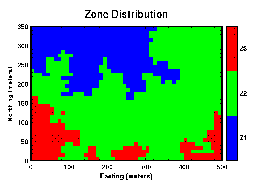

For this example, it is convienient to think of the green zone as being river channel sands and gravels, and the red and blue zone as being overbank clay deposits. There is little reason for the zones to be related, therefore they should be treated differently. Note, the same result could be attained by modeling the site twice and merging the results together.